Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 0
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 328 Tags: binanceIs Binance truly safe? Explore 5 key perspectives on security, community strength, the BNB ecosystem, and crisis-handling strategies of...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 278 Tags: application, blockchain, environment, knowledge, waterSummary: Water management faces significant challenges, including pollution, waste, and inefficient...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 332 Tags: amm, defi, dex, uniswapSummary Uniswap v3 is currently the gold standard for Automated Market Makers (AMMs), but it’s not...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 326 Tags: ccip, chainlink, cross-chain, integrate, oracle, solanaArticle Summary:On May 19, 2025, Chainlink officially launched its Cross-Chain Interoperability...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 339 Tags: metamask, walletSummary:MetaMask has introduced Smart Accounts, a feature that unlocks powerful capabilities like batched transactions, paying gas fees...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 298 Tags: optimism, upgradeSummary: Optimism has successfully implemented the Isthmus hardfork, bringing key features from Ethereum’s Pectra upgrade to the...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 266 Tags: bnb, etf, vaneckSummary:VanEck has officially filed an S-1 registration statement with the U.S. SEC to launch the first Binance...
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 296 Tags: worldcoinKey Points: Unexpected Suspension and Its Immediate Impact Indonesia’s Ministry of Communication and Digital Affairs has revoked the licenses...
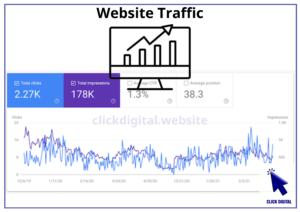
Số người xem bài viết (Post Views): 273 Tags: data, project No. Crypto Ticker Link website 03/2024 04/2024 05/2024 06/2024 07/2024 08/2024 09/2024 10/2024 11/2024 12/2024 01/2025 02/2025...